How to trade on BitMax.io: Futures Trading

In this article, we are going to explore the latest of BitMax.io’s product innovations – futures trading.
What is Futures Trading? (Futures Trading 101)
A futures contract is an agreement between two or more counterparties to buy or sell a commodity, currency or other financial instruments at a predetermined price at a specified time in the future. One side of the trade for a futures contract takes on a “long position” while the other side takes on a “short position.”
- The long position represents an obligation to purchase an asset from the short position on the futures contract’s expiration date.
- The short position represents an obligation to sell an asset to the long position on the futures contract’s expiration date.
The most intuitive way to explain futures trading is to contrast it with spot trading. For example, if a spot trader buys 1 BTC on a BTC/USDT order book, they are purchasing the asset from willing sellers at the prevailing market price (the spot price). Once the buyer and seller interact with one another, a trade is consummated, and the trade is settled immediately on the platform. The buyer’s trading account will be credited 1 BTC, and the seller’s trading account will be credited with an offsetting amount of USDT.
In contrast to spot trading which employs immediate post-trade delivery of assets, trading a futures contract does not involve the immediate settlement of the underlying asset. Instead, the contract dictates that the underlying asset will be settled or “delivered” at a future date. The date of settlement is referred to as “Expiration.” Futures contracts may expire on a monthly, or quarterly basis, for example.
Given bullish (positive) or bearish (negative) sentiment on the future price of the underlying asset, futures contracts may trade at a significant premium or discount to the spot market. As the date of expiration draws nearer and the future value of the underlying asset becomes clearer, spot and futures markets pricing will converge.
Futures are a zero-sum game. This means that the accounting gains made by one side of a trade are offset by the accounting losses incurred by the other side of a trade. For example, the profit that a long position receives from purchasing a contract at a lower price than the price of the underlying asset at expiration is exactly equal to the loss that the short position incurs.
In sum, futures contracts derive their value from an underlying asset and grant speculative traders and opportunity to take a view on the future price of an asset. As more sophisticated market participants enter the digital asset industry, derivatives trading platforms are seeing increasing popularity.
Understanding the Perpetual Futures Contract
The futures contract available on BitMax.io is a specific kind of futures contract known as a perpetual contract. At present, BitMax.io’s perpetual futures contract is only available for Bitcoin, although collateral can be posted in USDT, PAX, USDC, BTC, and ETH – this is its unique cross-asset collateral feature. Do note however that there will be a 2% discount on BTC and 5% discount on ETH as collateral (meaning you’ll have to post slightly more if using these two cryptos). This is to compensate for their inherent volatility.
A Perpetual Contract is a type of derivative product that combines aspects of futures trading and spot margin-trading. Key points of differentiation for trading Perpetual Contracts are:
No Expiration Date
Unlike futures contracts, perpetual contracts do not have an expiration date or a specified time in the future that buyers and sellers are obligated to settle a contract. Traders can hold long or short positions for as long as they’d like (i.e., “in perpetuity”), as long as they maintain sufficient margin to avoid liquidation. Margin collateral essentially serves as a means to verify an account’s “credit worthiness” by providing real assets to cover potential losses when trading on leverage.
Funding Mechanism
In lieu of cash or physical settlement, perpetual contracts employ “funding” to facilitate payouts between long and short positions at various intervals. BitMax.io facilitates funding once every 12 hours (at 0:00 a.m, and 12:00 p.m UTC). For example, if contract prices are trading at a discount to the underlying spot market, funding rates will be negative and short positions will pay long positions. Conversely, if contract prices are trading at a premium to the market, funding rates will be positive and long positions will pay short positions.
Price Correlation to Underlying Spot Market
Unlike settled futures contracts, which may trade at a significant premium or discount to the underlying spot market depending on the expiration date, perpetual contracts tend to be priced in line with underlying spot market prices. Convergence between the price of perpetual contracts and the underlying spot market is achieved by a funding mechanism that requires long or short positions to pay the opposing side based on any decoupling in price between the contract and the underlying spot market.
In this regard, funding serves as a marketplace incentive to encourage traders to take positions with the positive expected value (with regards to funding). This moves the price of the contract until it eventually converges with spot prices.
The Role of Leverage in BitMax.io’s Perpetual Futures Contract
BitMax.io’s futures trading platform offers its users very attractive leverage of up to 100x. Trading on leverage allows buyers and sellers to open positions after depositing only a fraction of the trade amount – in contrast, to spot trading which generally requires fully funded orders. Bullish traders with a positive outlook on the market can open long positions by buying contracts while bearish traders with a negative outlook on the market can open short positions by selling contracts. Leveraged trading can increase buying or selling power to allow for potentially higher returns. However, it can also magnify losses, and thus risk, as well.
For example, at 100x leverage, a 1% move in the contract price can either double a trader’s account value or drain the account completely. Hence why BitMax.io requires accounts to post collateral. Collateral determines an account’s Margin Rate (and thus the amount of leverage the user can trade with) as well as when the account is at risk of being auto liquidated.
Accordingly, the maximum amount of leverage available depends on the size of a user’s position. To open a leveraged contract on BitMax.io, an account must have an Account Margin Rate (Collateral / Position) that meets or exceeds the Initial Margin Rate. To maintain an open position on a leveraged contract on BitMax.io Futures, an account must have an Account Margin Rate that meets or exceeds the Maintenance Margin Rate.
The table below shows the initial margin you must post when you first open a trade, as well as the maintenance margin to keep the position open. As you can see, it is possible to open a trade with an initial margin of 1% (implying 100x leverage); however, the maintenance margin needed is only 60% of that. This makes it easier to keep leveraged positions open even in the event of an adverse market movement.
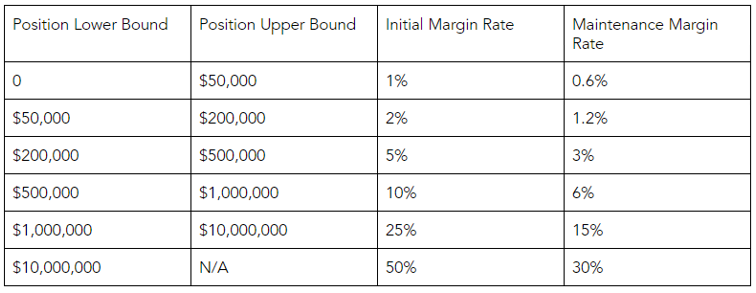
With just USD500, you can open a contract with a notional value of as high as USD50,000 (1% margin). However, as the notional values increase, the amount of leverage available decreases as well.
How to (Easily) Trade Perpetual Futures Contracts on BitMax.io
Now, let’s move into how to trade these perpetual futures contracts on the BitMax.io platform. Fortunately, just like BitMax.io’s other features, it’s very simple to use once you get the hang of it. It’s a testament to the team’s design acumen that the learning curve is so gentle.
To get started trading futures on BitMax.io, simply log in as normal and select ‘Futures’ from the homepage menu bar.

That will take you to the following interface.
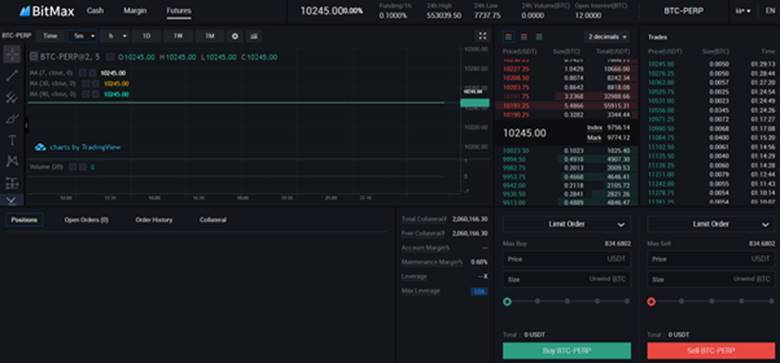
Note how you can easily switch between futures, cash, and margin trading.
Let’s take a closer look at the order book.
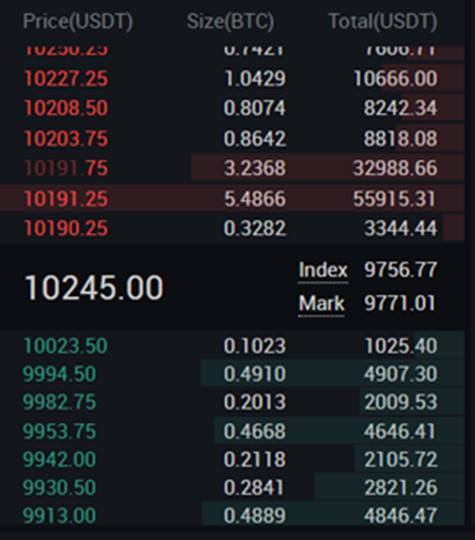
The red represents parties selling contracts (meaning you can buy them) and the green, the opposite. Note that due to the nature of the perpetual contracts, they are trading relatively close to the Bitcoin spot price, which you can see by looking at the ‘Index’ and ‘Mark’ values in the middle.
Now, let’s look at trading the futures contracts. Let’s assume I am bullish on Bitcoin, and thus I want to buy (go long) a contract. I can either manually fill out the left-hand column below or select one of the red sell orders from the order book, which automatically populates the details.
Those little green and red sliders you see are what allow you to adjust your leverage amounts. If you click the downward arrow next to the ‘Limit Order’, you will open a dropdown that shows you the other types of orders available.
And that’s all there is to it. If you want to unwind any position, just repeat the same process, but use the different colored boxes!
Conclusion: BitMax.io Continues to Turn the Complex Simple with Futures Trading
When you begin futures trading, you are diving into the vast ocean of financial derivatives. It seems intimidating, and many people may even reflexively avoid it. But one of BitMax.io’s strengths has always been in providing its users with as many features as possible (e.g. cross-asset collateralization) while maintaining simple, intuitive user experience.
The platform’s new futures trading functionality is no different. Traders seeking high leverage opportunities to benefit from the volatile Bitcoin market would do well to give BitMax.io serious consideration.



